series Part 1
From barter to digital cash.
Money has been part of human history for more than 5,000 years. From the origins of bartering to modern crypto money, this is how the system has evolved. At the dawn of humanity, bartering was used in lieu of money to buy goods. As man began to domesticate livestock, one of the earliest forms of barter included cattle, sheep, as well as vegetables and grain.
The first known currency was created by King Alyattes in Lydia, now part of Turkey, in around 600BC. The first coin ever minted features a roaring lion. Coins then evolved into bank notes around 1661 AD. “We have gold because we cannot trust governments,” President Herbert Hoover famously said in his statement in 1933 to Franklin D. Roosevelt’s inauguration.
The gold standard is a monetary system where a country’s currency or paper money has a value directly linked to gold. With the gold standard, countries were committed to convert their paper money into a fixed amount of gold. A country that uses the gold standard sets a fixed price for gold and buys and sells gold at that price. That fixed price is used to determine the value of the currency. The gold standard is not currently (2018) used by any government. Britain stopped using the gold standard in 1931 and the U.S. followed suit in 1933 and abandoned the remnants of the system in 1971. As World War II was coming to an end, the leading Western powers met to develop the Bretton Woods Agreement, which would be the framework for the global currency markets until 1971. Within the Bretton Woods system, most of the national currencies were valued in relation to the U.S. dollar, which was itself directly linked to gold. The dollar became the dominant reserve currency.
The gold standard was completely replaced by fiat money, a term used to describe currency that is issued by a government and must be accepted as a means of payment within its territory. (more about the gold standard: here). The first credit card was introduced in 1946.
The infographic below shows how money has developed from these early roots through to Apple’s instant iPhone payments and bitcoin — the world’s first decentralised blockchain-based cryptocurrency. Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency was born in the chaotic days of the last big financial crisis in 2008. The financial crisis of 2008 was, in part, due to unrealistic expectations of financial institutions. By accident or design — or a combination of the two — large financial institutions engaged in practices in which they assumed the outcome had no downside for them. By assuming the government would opt as a backstop, the bank’s actions were a good example of moral hazard and behavior of people and institutions who think they are given a free option.
How did moral hazard contribute to the 2008 financial crisis? Read more: here
This moral hazard lead to the creation of the first Peer to Peer payment protocol by Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin. Bitcoin opened a gateway to the new technology of the internet in value transfer by using blockchain. Although blockchain-based cryptocurrencies are in a embryonic age, they can assume all the functions of money: medium of exchange, measure of value, store of value, unit of account, a standard of postponed payment, the basis of credit.
Why do bitcoins have value?
Cryptocurrencies have value because they are useful as a form of money. Money is accepted because it is accepted (this is paradox of money). Crypto has the characteristics of money (durability, portability, fungibility, scarcity, divisibility, and recognizability) based on the properties of mathematics rather than relying on physical properties (like gold and silver) or trust in central authorities (like fiat currencies). In short, Bitcoin and other cryptos are backed by mathematics. With these attributes, all that is required for a form of money to hold value is trust and acceptance. In the case of crypto, this can be measured by its growing base of users (merchants, startups, individuals). As with all currency, bitcoin’s value comes only and directly from people willing to accept it as payment.
Although cryptocurrencies are in their infancy, they can represent all the functions of money: medium of exchange, measure of value, store of value, unit of account, a standard of postponed payment, the basis of credit. Functions of money? Read more: here
The most used function of the money is as medium of exchange and it is one of the most beneficial function that crypto can add value to people.
The advent of modern — digital — bartering has brought the system full circle.
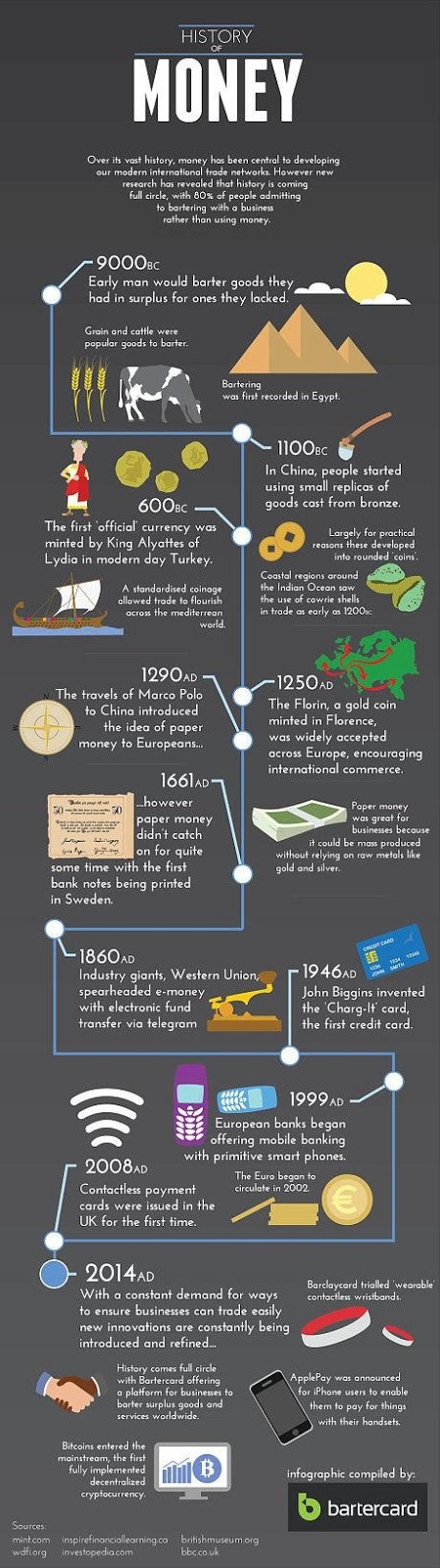
Source: here
This series is supported by the #MoneyInTheRightDirection Global Stablecoin Popularization and Education Movement backed by CorionX.
If you are a backer or philanthropist who are willing to contribute to the movement’s costs — do not hesitate to contact us by email or reach out to our official LinkedIn or Telegram group — we always appreciate your comments!
Stay tuned for the next Part.
Join our Telegram!
Follow Corion Foundation on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram and LinkedIn !
Stay tuned and follow the ‘Stablecoin Movement’ on Twitter, Medium, Facebook and Instagram!



